Coinbase Wallet allows you to transfer tokens to and from Layer 2 (L2) networks and sidechains such as Polygon, Arbitrum, and Base.
Layer 2 (L2) is a network or channel that sits on top of a Layer 1 (L1) network like Bitcoin or Ethereum. L2's are designed to enhance the speed and reduce the cost of performing transactions on a blockchain. L2s improve blockchain scalability by reducing the number of nodes or participants required to validate transactions within the L2 network, thereby reducing the time it takes to achieve consensus.
All confirmed transactions on an L2 are periodically batched together and submitted back to the L1 where they are validated as one large transaction and added to the next block on the L1 chain.
Lightning network is an L2 solution for the Bitcoin network. Arbitrum and Loopring are L2 scaling solutions for the Ethereum network. Polygon Network functions as both a L2 and a sidechain for the Ethereum network.
Base is an Ethereum Layer 2 (L2) chain that offers a safe, low-cost, developer-friendly way to build on-chain. Base is an L2 built on OP Stack in collaboration with Optimism.
A sidechain is an independent blockchain that connects to a main blockchain (which is also called a ‘mainchain’ or 'mainnet').
Sidechains allows developers more flexibility to construct their own parameters for how they want to operate their blockchain. This includes using alternative consensus mechanisms from the mainchain or optimizing for specific traits like speed, privacy, and token design or tokenomics.
Over a million Coinbase Wallet customers are using decentralized finance apps such as Uniswap, Compound and Aave, and NFT platforms like OpenSea and Zora.
However, there are often high transaction fees and long confirmation times. In addition, users with smaller transactions can be priced out of being able to participate in the open financial system. This has made the need for accessible scaling solutions even more important. This integration will allow for faster and cheaper transactions, and provide easier access to decentralized innovation.
Some potential cons with L2 or Sidechain networks include low liquidity, limited integration with exchanges and lengthy withdrawal times to transfer funds back to the mainchain/mainnet.
Visit Supported assets and networks to learn more about which L2s, side chains and alternative blockchains we support.
A blockchain bridge, otherwise known as a cross-chain bridge, connects two blockchains and allows users to send cryptocurrency from one chain to the other. For example, if you have Bitcoin but want to spend it like Ethereum, you can do this through a supported bridge.
With Coinbase Wallet app, you can connect to a bridge of your choice, to transfer funds between mainchains or a mainchain and L2 chain. To learn more, visit our help article: Bridging your crypto
Transacting on L2 networks is subject to network or miner fees. The fees you pay will be denominated in the networks native currency. For example, the Polygon chain facilitates transactions using MATIC as the main currency for fees. Therefore, to transact on this network, you will need sufficient MATIC funds in order to account for the fees.
There are other lesser-known but still EVM-compatible (Ethereum virtual machine) networks that also offer similar scalability solutions to popular L2 networks. Coinbase Wallet allows you to add a customer network RPC, in order to transact on the designated network.
To add a custom network on the Coinbase Wallet mobile app:
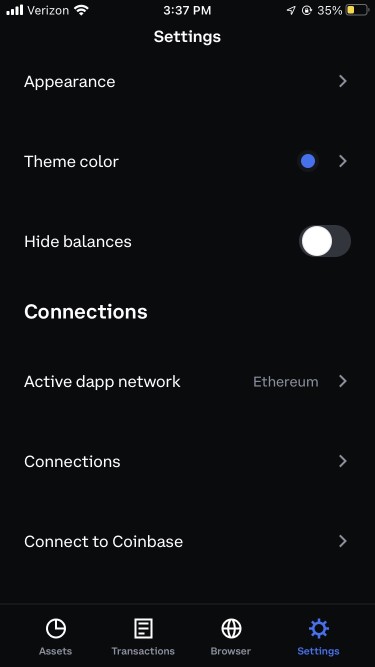
Select Settings
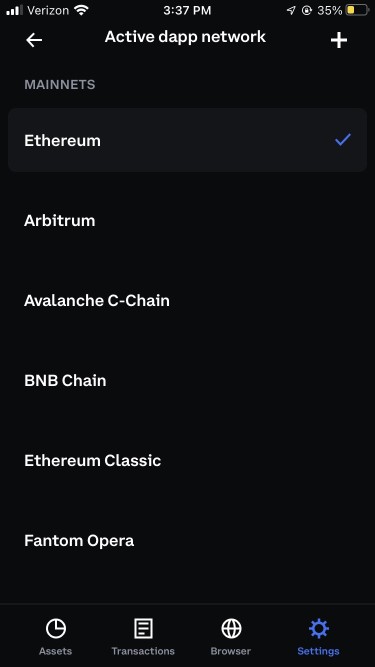
Select ‘Active dapp network’ (or ‘Default network’ on the Coinbase Wallet Extension).
Select the plus symbol on the top-right of your screen
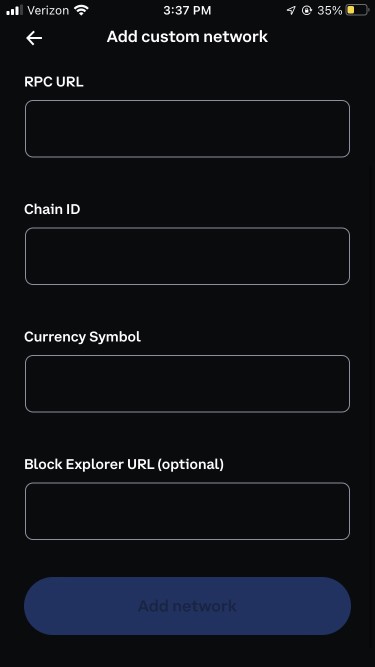
Complete designated fields, which are usually provided in a developer guide or doc. of the network in question
Once complete, select ‘Add network’
For a suggested list of currently available EVM blockchains you can refer to websites such as Chainlist.org.
Note: prior to interacting, thoroughly research the network in question and ensure it’s coming from a trusted operator. Some of these may pose as credible providers but can be deliberate attempts to compromise your funds and Wallet. While there is no guarantee, we advise that you understand the potential risks involved with this.
To verify a custom network, make sure you source the information for adding the network from the protocols official documentation page. Here is an example for the Harmony blockchain.